Did you know that the fastest-growing energy source in the world is solar power? In reality, thanks to advancing technology and declining costs over the past several years, the adoption of Solar Photovoltaic (PV) system designs has expanded tremendously. But, you must first comprehend the fundamentals in order to build and construct a solar photovoltaic system.
In this blog post, we will provide everything you need to know to understand the full scope of a solar photovoltaic system design. So let’s get started!
What is a Solar PV System?
A Solar Photovoltaic (PV) system is a complete electrical system that generates electricity from the sun’s energy. It consists of solar photovoltaic (PV) modules, batteries, an inverter, electrical wiring, and other components. Everything works together to convert the sun’s rays into usable electricity.
The PV modules contain cells that are made from materials like crystalline silicon or thin-film cells. When these cells are exposed to sunlight, they generate Direct Current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is then converted into Alternating Current (AC) electricity with the help of an inverter. This AC electricity can then be used to power your home or business.
Types of Solar PV Systems
You may notice various types of solar pelvic systems in modern residential homes, corporate buildings, and other types of structures. Despite where it is used, the followings are the most common types of solar PV systems,
- Grid-Connected Systems: A grid-connected system consists of PV modules, a power conditioner, a meter, and other electrical hardware. Everything in this system is connected to the utility grid. This type of system allows the user to send excess electricity generated from the PV array back to the utility grid for credit or net metering. This enables the user to store energy for later use.
- Stand-Alone Systems: Stand-alone systems are not connected to any other power source. Instead, they usually have a battery bank for energy storage. This type of system is ideal for remote locations where access to the grid is limited or nonexistent.
- Hybrid Systems: A hybrid system combines the technologies of both grid-connected and stand-alone systems. This type of system is best suited for users who want to generate their own electricity while having access to the grid if required.
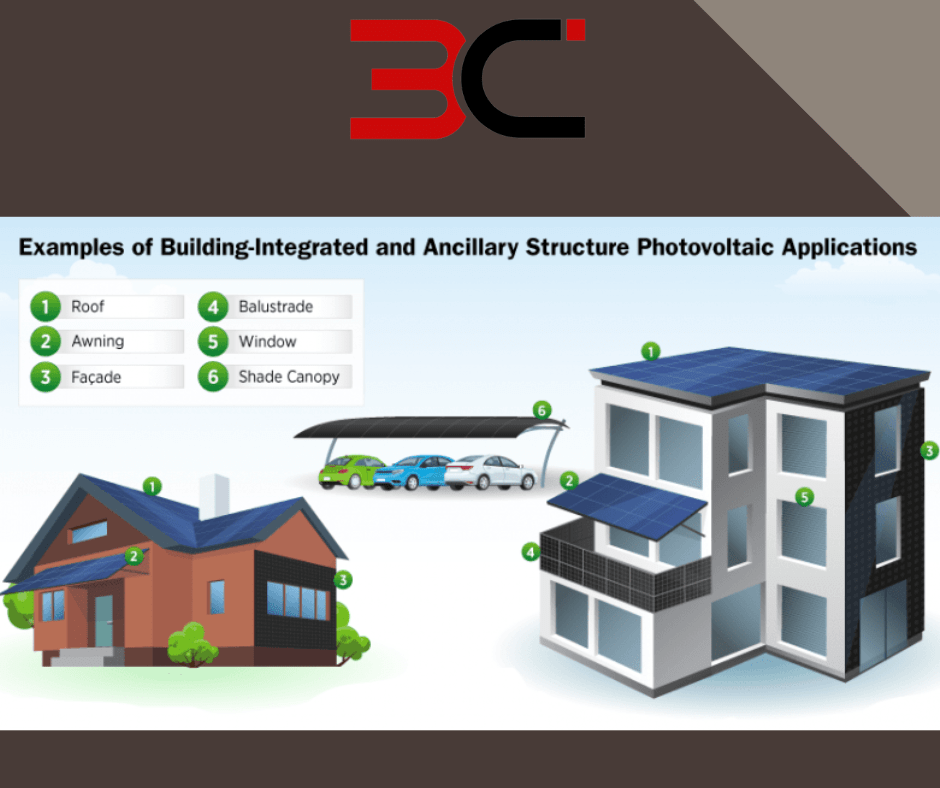
- Building-Integrated Systems: This type of solar PV system is integrated into the building structure itself. Building-integrated systems are typically used in commercial buildings. These systems provide the advantages of both aesthetics and efficiency.
Figure: Building Integrated PV, or BIPV
The Major Components of a Solar PV System
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) systems are composed of several components that work together to generate electricity from sunlight. Let’s look at the major components of Solar PV in detail:
- Solar Modules: These are the most essential part of a solar PV system, as they convert sunlight directly into electrical energy. Each module is made up of many individual solar cells, which are wired together and encapsulated in a weatherproof frame. The number of modules used will depend on the size of the system and the amount of electricity it is expected to produce.
- Inverters: These are used to convert the Direct Current (DC) electricity generated by the solar modules into Alternating Current (AC) electricity, which is what is used in homes and businesses. Depending on the type of system being installed, the inverter may be located in the main control unit or in an external enclosure.
You will find two types of inverters for solar PV systems in the market. They are
- Micro-inverters
- String inverters
- Charge Controllers: These are used to ensure batteries are not overcharged or damaged by sudden surges of power. They also regulate the flow of power between the solar modules and the batteries. Hence, it prevents any back-flow of electricity.
- Batteries: These are used to store any excess electricity generated by the solar modules for later use. Most battery systems consist of a set of deep-cycle lead-acid batteries. However, newer technologies such as lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly popular due to their lighter weight and longer lifespan.
- Racking Systems: These provide a secure method for mounting the solar modules in place. It will ensure that they stay securely fixed in all weather conditions. The type of racking used will depend on the type of roof or ground surface being used, as well as the load capacity of the system being installed.
Sizing a Solar PV System
This is an important part of ensuring that a solar PV system runs efficiently. The size of the system will determine how much electricity you can generate and how much you can save. When it comes to sizing a solar PV system, there are several factors to consider.
Let’s take a look at these factors:
- The first factor is the amount of energy you need. The total required energy is determined by your daily electricity use and the amount of sunlight available in your area. Generally speaking, the more power you need, the bigger the system needs to be.
- The second factor is the type of solar panel you plan on using. Different types of solar panels have different wattage ratings. It means they can produce different amounts of electricity. If you want to generate a certain amount of electricity, you need to choose the right type of solar panel.
- The third factor is the angle and direction of your roof or mounting surface. It is very important to angle your panels towards the sun in order to maximize the amount of sunlight they receive. Additionally, this ensures that your panels don’t get too hot, which can lead to decreased efficiency.
- The fourth factor is making sure that you have enough space for your solar PV system. The amount of space required will depend on the number of panels you plan on installing, as well as the size of each panel. Moreover, you need to factor in any other equipment if you plan on having them. This includes an inverter and battery storage.
A deep-cycle battery is the suggested battery type for solar PV installations. These batteries are made specifically to be cycled through charging and discharging again every day at a time at low power levels. You may compute the battery size as follows:
Battery Capacity (Ah) = Total Watt-hours per day used by appliances x Days of autonomy(0.85 x 0.6 x nominal battery voltage)
- Lastly, calculate the rating of the solar charge controllers. Generally, this rating is based on the amperage and voltage capabilities of solar charge controllers. Choose a solar charge controller that will work with your battery voltage and PV array. Usually, the capacity of a solar charge controller to manage the current is generated by a PV array.
The size of the controller for the series type is determined by the total PV input current given to the controller. It also depends on how the PV panels are set up.
The standard procedure for sizing a solar charge controller is to multiply the PV array’s short circuit current (ISC) by 1.3.
Solar charge controller rating = Total short circuit current of PV array x 1.3
Solar PV System Mounting
There are a few key considerations that need to be taken into account while mounting a solar PV system. The following are all important elements to consider:
The size and type of installation:
The two main types of solar PV system mounting are,
- Fixed
- Adjustable
Fixed systems are generally easier to install and require less maintenance, but they do not allow for the optimization of the system’s performance. On the other hand, adjustable systems are more difficult to install and require more maintenance. However, they offer better performance when conditions vary.
The materials and components:
When it comes to materials, aluminum is often the preferred choice for both fixed and adjustable mounts due to its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties. Stainless steel is also popular because it is stronger and more durable than aluminum, but it is more expensive. Other materials, such as wood, concrete, and plastic, can also be used, depending on the project requirements.
The process of mounting the system:
The actual mounting process can range from simple and straightforward to complicated and labor-intensive. A good rule of thumb is to always work with experienced professionals who can assess the particular requirements of your installation. They can also design the best possible mounting solution.
Bottom Line
A solar photovoltaic system can be a great way to power your home or business with clean, renewable energy. Designing and installing a system correctly is essential for getting the most out of your investment. Understanding the different types of systems and components will also ensure your system runs efficiently and safely.
With that said, you need to be aware of mounting different systems properly. With careful planning and execution, you can enjoy the many benefits of solar energy for years to come.